ConvNet을 TensorFlow로 구현하자 (MNIST)
July 20, 2019
해당 게시물은 Edwith에서 제공하는
머신러닝과 딥러닝 BASIC을 듣고 요약 정리한 글입니다.
사용할 CNN 구성
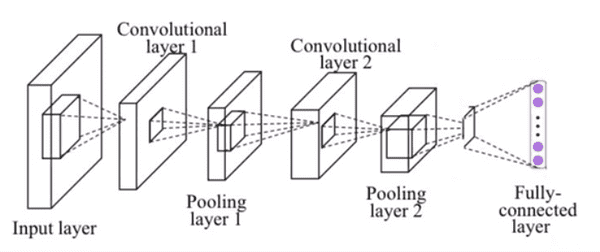
- Conv Layer 1
- Pooling Layer 1
- Conv Layer 2
- Pooling Layer 2
- Fully-Connected Layer
사용할 모듈 추가
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import randomMNIST 데이터 불러오기
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)상수 정의
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)입력값 placeholder 선언
n개의 크기의 흑백 이미지를 입력
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
X_img = tf.reshape(X, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])Conv Layer 1 구성
필터의 크기는 임읠로 정할 수 있다.
아래의 코드에서는 크기의 필터 32개 사용
padding이 SAME인 경우 weight의 크기에 상관없이 출력값은 입려값의 크기와 같다.
첫번째 Conv Layer를 통과난 후의 Tensor의 크기는 (?, 28, 28, 32)다.
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 32], stddev=0.01))
L1 = tf.nn.conv2d(X_img, W1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
print(L1)Tensor("Conv2D:0", shape=(?, 28, 28, 32), dtype=float32)Pooling Layer 1 구성
Pooling Layer를 구성할 때도 커널 사이즈를 임의로 정할 수 있다.
아래의 코드에서는 크기의 커널 사용
stride가 2이고 padding이 SAME이기 때문에 출력값은 의 크기다.
L1 = tf.nn.relu(L1)
print(L1)
L1 = tf.nn.max_pool(L1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
print(L1)Tensor("Relu:0", shape=(?, 28, 28, 32), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool:0", shape=(?, 14, 14, 32), dtype=float32)Conv Layer 2 구성
앞의 Layer의 출력값의 크기는 임을 기억
이전의 Conv Layer와 마찬가지로 필터의 크기는 임의로 지정이 가능하다.
Conv Layer 2에서는 크기의 필터를 64개 사용
Conv Layer 2를 통과난 후의 Tensor의 크기는 (?, 14, 14, 64)다.
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 32, 64], stddev=0.01))
L2 = tf.nn.conv2d(L1, W2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
print(L2)Tensor("Conv2D_1:0", shape=(?, 14, 14, 64), dtype=float32)Pooling Layer 2 구성
아래의 코드에서는 크기의 커널 사용
stride가 2이고 padding이 SAME이기 때문에 출력값은 의 크기다.
입체적인 데이터를 펼치기 위해 reshape함수 사용, 사용 후 크기는 (?, 3136)이다.
L2 = tf.nn.relu(L2)
print((L2))
L2 = tf.nn.max_pool(L2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
print((L2))
L2_flat = tf.reshape(L2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
print((L2_flat))Tensor("Relu_1:0", shape=(?, 14, 14, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool_1:0", shape=(?, 7, 7, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("Reshape_1:0", shape=(?, 3136), dtype=float32)Fully-Connected Layer 구성
Weight의 크기는 [입력값, 출력값]이기 때문에 [7 * 7 * 64, 10]과 같다.
아래의 코드에서는 xavier_initializer를 사용해 Weight을 초기화했다.
Bias의 크기 또한 출력값의 크기와 같기 때문에 [10]이다.
W3 = tf.get_variable(
"W3", shape=[7 * 7 * 64, 10],initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer()
)
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
logits = tf.matmul(L2_flat, W3) + b손실함수와 최적화 방법 정의
예측해야하는 값이 10개이기 때문에 Softmax classfier를 사용한다.
아래의 코드에서는 최적화 함수로 AdamOptimizer을 사용했다.
cost = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=Y)
)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)Session 초기화
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())모델 학습 진행
print("------ 학습 시작 ------ ")
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict = {X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys}
c, _, = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict)
avg_cost += c / total_batch
print('Epoch :', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print("------ 학습 종료 ------")------ 학습 시작 ------
Epoch : 0001 cost = 0.342477704
Epoch : 0002 cost = 0.096237179
Epoch : 0003 cost = 0.071659406
Epoch : 0004 cost = 0.058874942
Epoch : 0005 cost = 0.049123090
Epoch : 0006 cost = 0.044309922
Epoch : 0007 cost = 0.038458925
Epoch : 0008 cost = 0.033626531
Epoch : 0009 cost = 0.029662574
Epoch : 0010 cost = 0.026359648
Epoch : 0011 cost = 0.024228121
Epoch : 0012 cost = 0.021708502
Epoch : 0013 cost = 0.017998194
Epoch : 0014 cost = 0.016982747
Epoch : 0015 cost = 0.014680203
------ 학습 종료 ------모델 테스트 및 정확도 확인
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print(
'Accuracy:', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels})
)
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r:r + 1], 1)))
print(
"Prediction: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(logits, 1), feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r:r + 1]})
)Accuracy: 0.9872
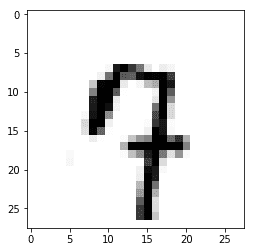
Label: [7]
Prediction: [7]예측한 정수 그리기
plt.imshow(
mnist.test.images[r:r + 1].reshape(28, 28),
cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest'
)
plt.show()