Drop Out을 사용해 MNIST 정확도 높이기
June 03, 2019
해당 게시물은 Edwith에서 제공하는
머신러닝과 딥러닝 BASIC을 듣고 요약 정리한 글입니다.
사용할 모듈 추가
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import randomMNIST 데이터 불러오기
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)상수 정의
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)입력값 placeholder 선언
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])keep_prob 선언
tensorflow 1.0부터는 keep_prob를 사용한다.
이것은 전체 네트워크중 몇 퍼센트를 keep할 것인지 결정한다.
학습과정에서는 0.5 ~ 0.7정도의 수치를 keep하고
테스트과정에서는 반드시 전체(1)를 keep해야 한다.
따라서 keep_prob를 placeholder로 선언한다.
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)Neural Network Layer 구성
Drop Out을 사용할 하나의 Layer를 추가로 구성하면 된다.
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", shape=[784, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
L1 = tf.nn.dropout(L1, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2) + b2)
L2 = tf.nn.dropout(L2, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L2, W3) + b3)
L3 = tf.nn.dropout(L3, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W4 = tf.get_variable("W4", shape=[512, 512],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b4 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([512]))
L4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L3, W4) + b4)
L4 = tf.nn.dropout(L4, keep_prob=keep_prob)
W5 = tf.get_variable("W5", shape=[512, 10],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b5 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10]))
hypothesis = tf.matmul(L4, W5) + b5손실함수와 최적화 방법 정의
cost = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=hypothesis, labels=Y)
)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)Session 초기화
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())모델 학습 진행
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict = {X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 0.7}
c, _ = sess.run([cost, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict)
avg_cost += c / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning Finished!')Epoch: 0001 cost = 0.468633001
Epoch: 0002 cost = 0.170478383
Epoch: 0003 cost = 0.131077586
Epoch: 0004 cost = 0.108677959
Epoch: 0005 cost = 0.096312569
Epoch: 0006 cost = 0.082181592
Epoch: 0007 cost = 0.078254419
Epoch: 0008 cost = 0.069326370
Epoch: 0009 cost = 0.062080975
Epoch: 0010 cost = 0.055655396
Epoch: 0011 cost = 0.057310239
Epoch: 0012 cost = 0.055785087
Epoch: 0013 cost = 0.052270090
Epoch: 0014 cost = 0.048582647
Epoch: 0015 cost = 0.044075073
Learning Finished!모델 테스트 및 정확도 확인
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print(
'Accuracy:',
sess.run(
accuracy,
feed_dict={
X: mnist.test.images,
Y: mnist.test.labels,
keep_prob: 1
}
)
)Accuracy: 0.9813Drop out을 사용한 결과 97%의 정확도에서
98%까지의 정확도 까지 올리는데에 성공하였다.
임의의 정수 예측하기
r = random.randint(0, mnist.test.num_examples - 1)
print("Label: ", sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[r:r+1], 1)))
print(
"Prediction: ",
sess.run(
tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1),
feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[r:r+1], keep_prob:1}
)
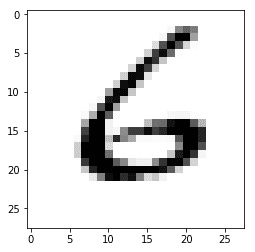
)Label: [6]
Prediction: [6]예측한 정수 그리기
plt.imshow(
mnist.test.images[r:r + 1].reshape(28, 28),
cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest'
)
plt.show()
Optimizer
여러가지의 Optimizer가 존재하지만 여러가지를
테스트해서 사용하는 것이 좋지만 통상적으로 Adam으로 시작하는것이 좋다.
