Lab 9-2:Tensor Board로 딥네트웍 들여다보기
May 22, 2019
해당 게시물은 Edwith에서 제공하는
머신러닝과 딥러닝 BASIC을 듣고 요약 정리한 글입니다.
Tensorboard
진행사항을 한눈에 볼 수 있도록 해준다.
TF Graph 시각화가 가능하다.
Tensorboard 사용 단계
-
어떤 Tensor를 logging할지 결정
w2_hist = tf.summary.histogram("weight2", W2) cost_summ = tf.summary.scalar("cost", cost) -
logging할 데이터를 merge
summary = tf.summary.merge_all() -
Summary(logging한 데이터)를 어디에 기록할지 설정
wrtier = tf.summary.FileWriter("./images/2019-05-23/logs") wrtier.add_graph(sess.graph) -
Session을 열어 Summary실행 및 파일에 기록
s, _ = sess.run([summary, optimizer], feed_dict=feed_dict) writer.add_summary(s, global_step=global_step) -
터미널에서 Tensorboard명령어 실행
tensoorboard --logdir=./images/2019-05-23/logs
Logging할 데이터
값이 하나(scalar)일 경우 tf.summary.scalar사용
값이 여러개(vector)일 경우 tf.summary.histogram사용
Tensor 그래프 그리기
Tensor그래프를 한번에 펼쳐놓으면 보기 힘들기 때문에
Tensorboard의 tf.name_scope함수를 이용해 계층별 정리
여러개의 값으로 비교해보고 싶을 때
ex) learningrate = 0.1 vs learningrate 0.01
Multiple runs 사용
log를 저장하는 dir경로를 다르게 주고
부모의 디렉토리의 경로로 그래프를 실행
logs
├─ run0_1
├─ run0_01
└─ run0_001위와 같은 경우
tensorboard --logidr=./images/2019-05-23/logs/run0_1
tensorboard --logidr=./images/2019-05-23/logs/run0_01
tensorboard --logidr=./images/2019-05-23/logs/run0_01
의 명령어로 Tensorboard를 실행시킬 수 있지만
tensorboard --logidr=./images/2019-05-23/logs와 같이
상위 디렉토리로 Tensorboard를 실행시키면 비교가 가능
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x_data = np.array(
[
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]
],
dtype=np.float32
)
y_data = np.array(
[
[0],
[1],
[1],
[0]
],
dtype=np.float32
)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 2], name="x")
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name="y")
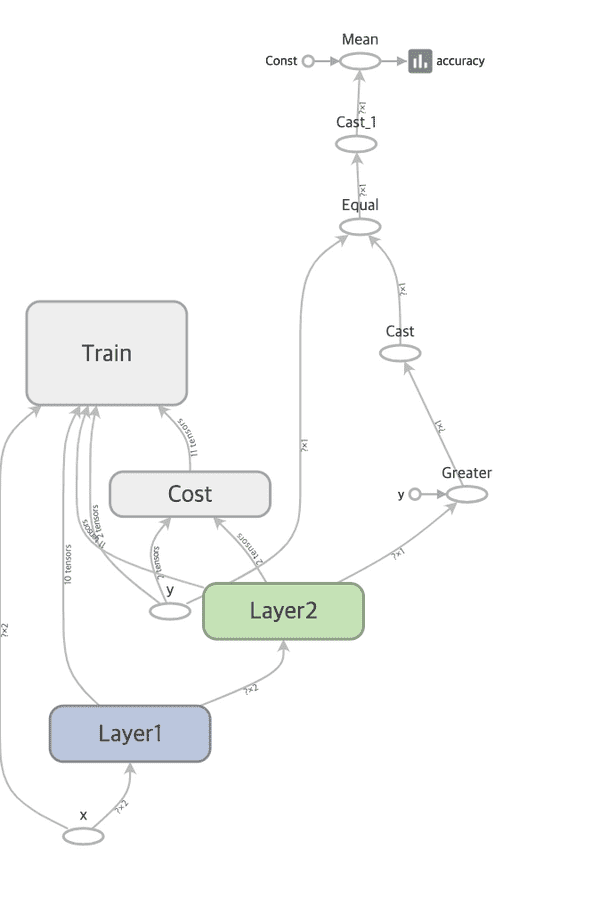
with tf.name_scope("Layer1"):
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 2]), name="weight_1")
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2]), name="bias_1")
layer1 = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(X, W1) + b1)
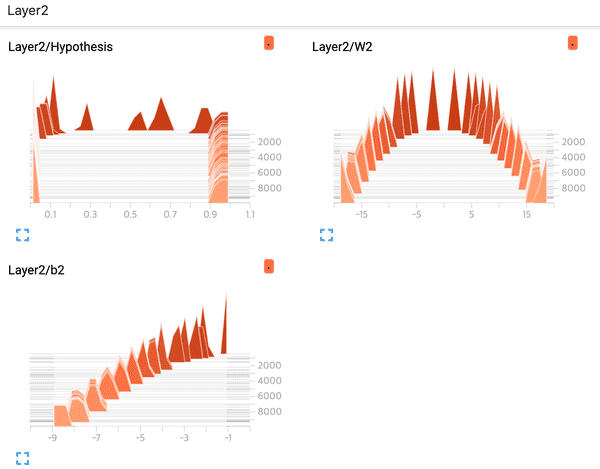
tf.summary.histogram("W1", W1)
tf.summary.histogram("b1", b1)
tf.summary.histogram("Layer1", layer1)
with tf.name_scope("Layer2"):
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1]), name="weight_2")
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name="bias_2")
hypothesis = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(layer1, W2) + b2)
tf.summary.histogram("W2", W2)
tf.summary.histogram("b2", b2)
tf.summary.histogram("Hypothesis", hypothesis)
with tf.name_scope("Cost"):
cost = -tf.reduce_mean(Y * tf.log(hypothesis) + (1 - Y) * tf.log(1 - hypothesis))
tf.summary.scalar("Cost", cost)
with tf.name_scope("Train"):
train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(cost)
predicted = tf.cast(hypothesis > 0.5, dtype=tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(predicted, Y), dtype=tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", accuracy)
with tf.Session() as sess:
merged_summary = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./images/2019-05-23/xor_logs")
writer.add_graph(sess.graph)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(10001):
_, summary, cost_val = sess.run(
[train, merged_summary, cost], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data}
)
writer.add_summary(summary, global_step=step)
if step % 1000 == 0:
print(step, cost_val)
h, p, a = sess.run(
[hypothesis, predicted, accuracy], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data}
)
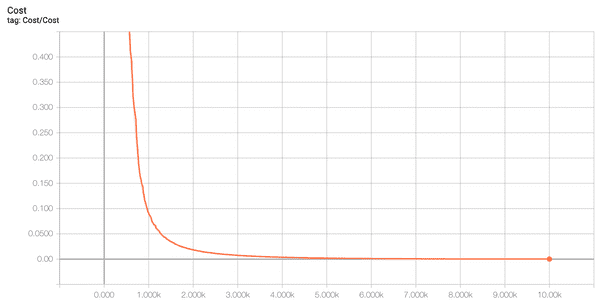
print(f"\nHypothesis:\n{h} \nPredicted:\n{p} \nAccuracy:\n{a}")0 1.0360026
1000 0.08819285
2000 0.01809669
3000 0.007408534
4000 0.0037033758
5000 0.0020230967
6000 0.0011570905
7000 0.0006789303
8000 0.00040425535
9000 0.00024286224
10000 0.00014668413
Hypothesis:
[[2.3283975e-04]
[9.9987853e-01]
[9.9987864e-01]
[1.1060548e-04]]
Predicted:
[[0.]
[1.]
[1.]
[0.]]
Accuracy:
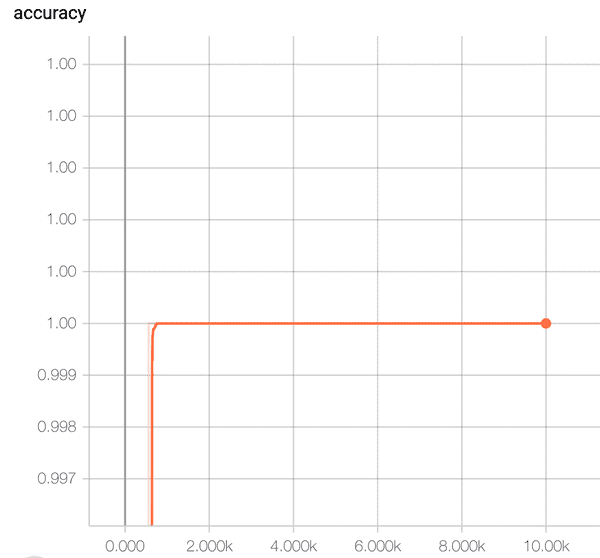
1.0XOR 문제 Log
- Cost
- Accuracy
- Graph
- Layer1 Distribution
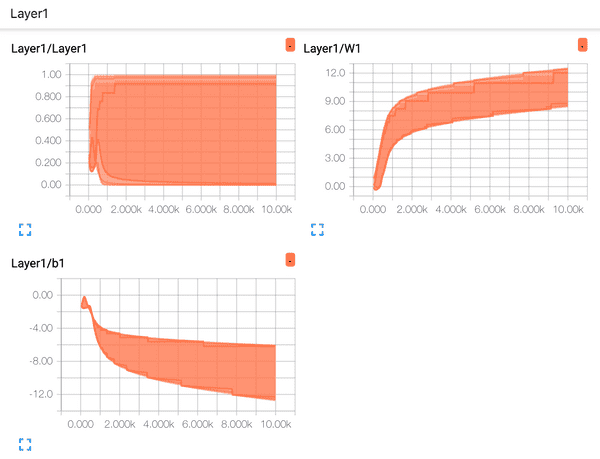
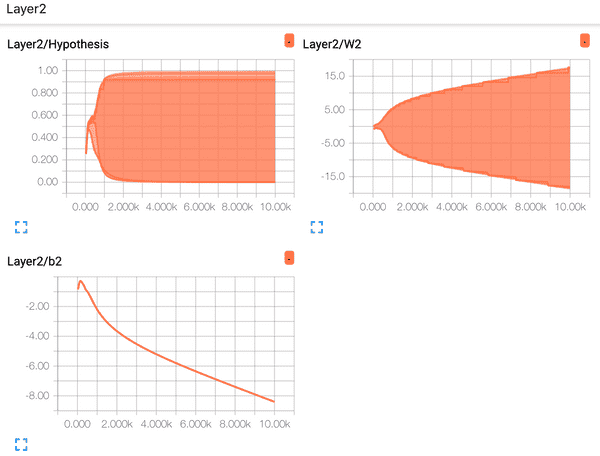
- Layer2 Distribution
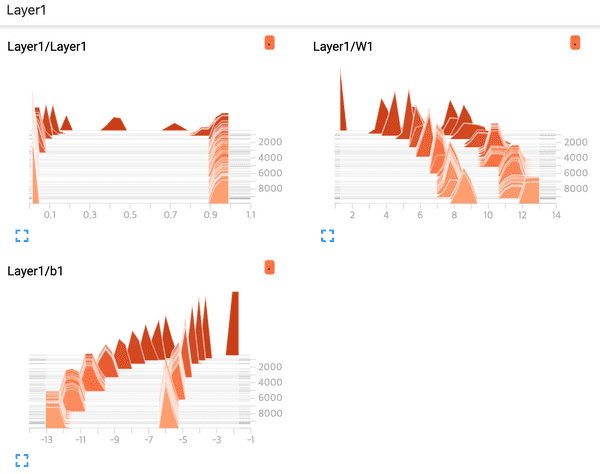
- Layer1 Histogram
- Layer2 Histogram