Linear Regression 의 cost 최소화의 TensorFlow 구현
January 04, 2019
해당 게시물은 Edwith에서 제공하는
머신러닝과 딥러닝 BASIC을 듣고 요약 정리한 글입니다.
Simplified hypothesis
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
X = [1, 2, 3]
Y = [1, 2, 3]
W = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# Our hypothesis for linear model X * W
hypothesis = X * W
# cost/loss function
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
# Launch the graph in a session
sess = tf.Session()
# Variables for plotting cost function
W_history = []
cost_history = []
for i in range(-30, 50):
curr_W = i * 0.1
curr_cost = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={W: curr_W})
W_history.append(curr_W)
cost_history.append(curr_cost)
# Show the cost function
plt.plot(W_history, cost_history)
plt.show()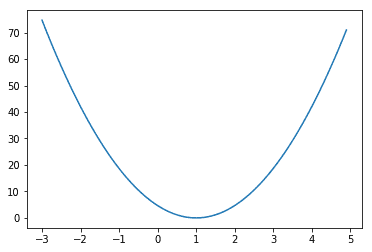
Gradient descent
import tensorflow as tf
x_data = [1, 2, 3]
y_data = [1, 2, 3]
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='weight')
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# Our hypothesis for linear model X * W
hypothesis = X * W
# cost/loss function
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
# Minimize : Gradient Descent using derivative
# W -= learning_rate * derivative
learning_rate = 0.1
gradient = tf.reduce_mean((W * X - Y) * X)
descent = W - learning_rate * gradient
update = W.assign(descent)
# Launch the graph in a session.
sess = tf.Session()
# Initializes global variables in the graph.
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(21):
sess.run(update, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
print(step, sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data}), sess.run(W))0 12.285609 [-0.6225382]
1 3.4945729 [0.13464624]
2 0.99401206 [0.53847796]
3 0.28274122 [0.75385493]
4 0.08042419 [0.8687226]
5 0.02287622 [0.9299854]
6 0.0065070093 [0.9626589]
7 0.0018508838 [0.9800847]
8 0.00052647345 [0.9893785]
9 0.00014975447 [0.9943352]
10 4.2596832e-05 [0.99697876]
11 1.2117175e-05 [0.99838865]
12 3.4466948e-06 [0.9991406]
13 9.802366e-07 [0.9995417]
14 2.7886367e-07 [0.99975556]
15 7.9282884e-08 [0.99986964]
16 2.2523963e-08 [0.9999305]
17 6.4054433e-09 [0.9999629]
18 1.8274401e-09 [0.9999802]
19 5.2067267e-10 [0.99998945]
20 1.4516388e-10 [0.9999944]Output when W = 5
- 경사하강법이 잘 되는지 테스트
- 오른쪽에서 하강
import tensorflow as tf
# tf Graph Input
X = [1, 2, 3]
Y = [1, 2, 3]
# Set wrong model weights
W = tf.Variable(5.0)
# Linear model
hypothesis = X * W
# cost/Loss function
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
# Minimize : Gradient Descent Magic
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
# Launch the graph in a session
sess = tf.Session()
# Initializes global variables int he graph
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(100):
print(step, sess.run(W))
sess.run(train)0 5.0
1 1.2666664
2 1.0177778
3 1.0011852
4 1.000079
5 1.0000052
6 1.0000004
7 1.0
8 1.0
9 1.0
10 1.0
...
90 1.0
91 1.0
92 1.0
93 1.0
94 1.0
95 1.0
96 1.0
97 1.0
98 1.0
99 1.0Output when W = -3
- 경사하강법이 잘 되는지 테스트
- 왼쪽에서 하강
import tensorflow as tf
# tf Graph Input
X = [1, 2, 3]
Y = [1, 2, 3]
# Set wrong model weights
W = tf.Variable(-3.0)
# Linear model
hypothesis = X * W
# cost/Loss function
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
# Minimize : Gradient Descent Magic
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
# Launch the graph in a session
sess = tf.Session()
# Initializes global variables int he graph
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(100):
print(step, sess.run(W))
sess.run(train)0 -3.0
1 0.7333336
2 0.98222226
3 0.9988148
4 0.99992096
5 0.9999947
6 0.99999964
7 0.99999994
8 1.0
9 1.0
10 1.0
...
90 1.0
91 1.0
92 1.0
93 1.0
94 1.0
95 1.0
96 1.0
97 1.0
98 1.0
99 1.0Optional : computegradient and applygradient
- Gradient를 수정하고 싶을 때 사용
compute_gradients()함수를 사용해cost에 알맞는gradient계산- 계산한
gradient를apply_gradients()함수 사용으로gradient적용
import tensorflow as tf
# tf Graph Input
X = [1, 2, 3]
Y = [1, 2, 3]
# Set wrong model weights
W = tf.Variable(5.)
# Linear model
hypothesis = X * W
# Manual gradient
gradient = tf.reduce_mean((W * X - Y) * X) * 2
# cost/Loss function
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - Y))
# Minimize : Gradient Descent Magic
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
# Get gradients
gvs = optimizer.compute_gradients(cost, [W])
# Apply gradients
apply_gradients = optimizer.apply_gradients(gvs)
# Launch the graph in a session
sess = tf.Session()
# Initializes global variables int he graph
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(100):
print(step, sess.run([gradient, W, gvs]))
sess.run(apply_gradients)0 [37.333332, 5.0, [(37.333336, 5.0)]]
1 [2.4888866, 1.2666664, [(2.4888866, 1.2666664)]]
2 [0.1659259, 1.0177778, [(0.1659259, 1.0177778)]]
3 [0.011061668, 1.0011852, [(0.011061668, 1.0011852)]]
4 [0.00073742867, 1.000079, [(0.00073742867, 1.000079)]]
5 [4.895528e-05, 1.0000052, [(4.8955284e-05, 1.0000052)]]
6 [3.0994415e-06, 1.0000004, [(3.0994415e-06, 1.0000004)]]
7 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
8 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
9 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
10 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
...
90 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
91 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
92 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
93 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
94 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
95 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
96 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
97 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
98 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]
99 [0.0, 1.0, [(0.0, 1.0)]]